 Hair is far more complex than it appears on the
surface. We all know that it not only plays a vital
role in the appearance of both men and women, but
it also helps to transmit sensory information as
well as create gender identification.
Hair is far more complex than it appears on the
surface. We all know that it not only plays a vital
role in the appearance of both men and women, but
it also helps to transmit sensory information as
well as create gender identification.
The Origins of Hair
By week 22, a developing fetus has all of its hair
follicles formed. At this stage of life there are
about 5 million hair follicles on the body. There
are a total of one million on the head, with one
hundred thousand of those follicles residing on
the scalp. This is the largest number of hair follicles
a human will ever have, since we do not generate
new hair follicles anytime during the course of
our lives. Most people will notice that the density
of scalp hair is reduced as they grow from childhood
to adulthood. The reason: Our scalps expand as we
grow.
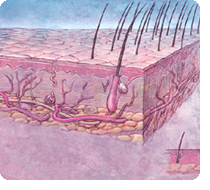
Hair Follicles
Hair has two distinct structures - first, the follicle
itself, which resides in the skin, and second, the
shaft, which is what is visible above the scalp.
The hair follicle is a tunnel-like segment of the
epidermis that extends down into the dermis. The
structure contains several layers that all have
separate functions. At the base of the follicle
is the papilla, which contains capillaries, or tiny
blood vessels that nourish the cells. The living
part of the hair is the very bottom part surrounding
the papilla, called the bulb. The cells of the bulb
divide every 23 to 72 hours, remarkably faster than
any other cell in the body.
Two sheaths, an inner and outer sheath, surround
the follicle. These structures protect and form
the growing hair shaft. The inner sheath follows
the hair shaft and ends below the opening of a sebaceous
(oil) gland, and sometimes an apocrine (scent) gland.
The outer sheath continues all the way up to the
gland. A muscle called an erector pili muscle attaches
below the gland to a fibrous layer around the outer
sheath. When this muscle contracts, it causes the
hair to stand up which also causes the sebaceous
gland to secrete oil.
The sebaceous gland is vital because it produces
sebum, which conditions the hair and skin. After
puberty our body produces more sebum but as we age
we begin to make less sebum. Women have far less
sebum production than men do as they age.
Hair Shafts
The hair shaft is made of a hard protein called
keratin and is made in three layers. This protein
is actually dead, so the hair that you see is not
a living structure. The inner layer is the medulla.
The second layer is the cortex and the outer layer
is the cuticle. The cortex makes up the majority
of the hair shaft. The cuticle is a tightly formed
structure made of shingle-like overlapping scales.
It is both the cortex and the medulla that holds
the hair's pigment, giving it its color.
Hair Growth Cycle
Hair on the scalp grows about .3 to .4 mm/day or
about 6 inches per year. Unlike other mammals, human
hair growth and shedding is random and not seasonal
or cyclical. At any given time, a random number
of hairs will be in one of three stages of growth
and shedding: anagen, catagen, and telogen.
Anagen
Anagen is the active phase of the hair. The cells
in the root of the hair are dividing rapidly. A
new hair is formed and pushes the club hair (a hair
that has stopped growing or is no longer in the
anagen phase) up the follicle and eventually out.
During this phase the hair grows about 1 cm every
28 days. Scalp hair stays in this active phase of
growth for two to six years.
Some people have difficulty growing their hair beyond
a certain length because they have a short active
phase of growth. On the other hand, people with
very long hair have a long active phase of growth.
The hair on the arms, legs, eyelashes, and eyebrows
have a very short active growth phase of about 30
to 45 days, explaining why they are so much shorter
than scalp hair.
Catagen
The catagen phase is a transitional stage and about
3% of all hairs are in this phase at any time. This
phase lasts for about two to three weeks. Growth
stops and the outer root sheath shrinks and attaches
to the root of the hair. This is the formation of
what is known as a club hair.
Telogen
Telogen is the resting phase and usually accounts
for 6% to 8% of all hairs. This phase lasts for
about 100 days for hairs on the scalp and longer
for hairs on the eyebrow, eyelash, arm, and leg.
During this phase, the hair follicle is completely
at rest and the club hair is completely formed.
Pulling out a hair in this phase will reveal a solid,
hard, dry, white material at the root. About 25
to 100 telogen hairs are shed normally each day
|
 |
|
